CYBER TRAINING FOR BUSINESSES
In 2019, a company fell victim to ransomware every 14 seconds.
That statistic alone should convince you to set up cybersecurity training for your employees. However, before you run down the hallway into the company’s c-suite offices to present your idea, we’d like to give you some more facts about why, when, and what to train employees on.
Or if you happen to be the decision maker for the company, NorthEast Insurance would like to convince you why cyber training for employees is crucial to the security of your business.
THE WHY
Consider this: If your employees don’t know anything about a security threat, then how can they stop it, report it or deal with it?
If your answer was that they can’t, then you’d be correct. Even though technology has reached nearly every part of our lives, there’s a startling fact we want you to know.
IT’S EMPLOYEES, NOT THE TECHNOLOGIES, THAT ARE THE MOST COMMON ENTRY POINTS FOR PHISHING SCAMS.
First step in your journey to training your employees is to accept that employees are humans and they will make mistakes.
THE WHEN
When should you train employees? Immediately and frequently.
Make training mandatory for the new employees to show new hires how much the company cares for cybersecurity. With the right training course, not only will they know more about modern cyber threats at work but also in their personal technology use as well. It’s a win-win for everyone.
Furthermore you should ensure the training course offered is updated frequently enough so your employees, when they do take the course, aren’t getting outdated information.
People can learn healthy internet habits through repetition. This is why requiring employees to take the course annually will keep their minds fresh and knowledgeable with cybersecurity.
THE WHAT
Keep in mind that it’s not just the company’s information at stake, it’s your customers’ information as well. Any type of cybersecurity breach not only could ruin the financial lives of you and others, but it also ruins the business’s reputation.
Fact of the matter is that you and your employees are the primary line of defense in preventing bad things from happening in your company and to yourself.
HERE IS A LIST OF THREATS YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT:
PHISHING ATTACKS:
Email messages designed to collect sensitive information from you. Information could include your logins, credit cards, and your Social Security number. These emails pretend to be from a trustworthy site like a bank or shipping company. They are designed to fool victims into believing the emails are genuine, going as far as using official corporate logos and other company identifiers.
WATERING HOLES:
This is a type of social engineering attack where criminals identify websites to target based on ones you visit on a regular basis. They infect the website as soon as you go onto it and you may not even notice malware downloading onto your computer or device.
Social engineering is an attack that relies on human interaction and often involves manipulating people into breaking normal security procedures and best practices in order to gain access to systems and networks.
MALICIOUS INTERNET ADVERTISING (MALVERTISING):
Malware that is distributed through online advertising. It can appear in any advertisement on any site, even the ones you visit as part of your everyday Internet browsing. Usually malvertising installs a piece of code which sends your computer to illegal servers. This server then scans your computer for its location, what software is installed and then chooses which malware will be most effective. All it takes is one click on the ad for malware or any other cyber threat to end up on your device or computer.
USER ERRORS:
Most malware or compromising code ends up on a computer because the user has chosen to install something that addresses a need they have. Which is exactly why it’s so important to vet the program or software you want to install. User error is the main reason why cyber training is so important.
MOBILE COPYCAT APPS:
Nearly all mobile devices have access to an online store to buy and download apps. As much as you’d like to believe those devices are safe, they’re not. This is especially true for third-party app stores as they have less restrictions and standards for the apps they put in their inventory. Even Google Play and the Apple App Store have their slip ups.
RANSOMWARE:
This one is exactly what it sounds like. Ransomware is a type of malware that demands a ransom be paid for access to your own files and computer, otherwise the attacker will delete everything or never give you access again. It sounds scary, we know. Especially since its one of the more common cyber attacks in the past few years.
SPEARPHISHING EMAILS:
These are targeted phishing attacks usually directed at a small group or demographic within your company. Because it’s so targeted, the email can be more believable and has a higher open rate.
REMOTE USERS WITH ACCESS TO CORPORATE RESOURCES:
If you don’t take the correct security precautions when accessing company files or networks, then you’re leaving an open door to those who want to do harm. This is exactly why it’s so important to vet and keep track of the technologies that your remote employees use.
MOBILE MALWARE:
Similarly mobile devices have a high rate of being infected with malware. The more tablets or smartphones connected to company networks or computers, the higher chance of malware spreading throughout the company.
COMPROMISED SEARCH ENGINE QUERIES:
Even though you may think search engines are secure, there’s always a possibility that a cyber criminal can infect your searches. The way this works is that they force your browser to display a search query screen with links to dangerous sites, usually filled with malware.
WE’D BE REMISS IF WE DIDN’T DISCUSS WAYS IN WHICH YOU CAN PROTECT YOURSELVES AND YOUR EMPLOYEES IN THIS POST, SO LET’S DIVE IN DEEPER.
PASSWORDS:
EMPLOY STRONG PASSWORDS
The general rule is that the longer and greater the variety of characters a password contains, the stronger it is. One great tool to try is the website howsecureismypassword.net (and if you’re worried about that site getting hacked then view it in private browsing mode).
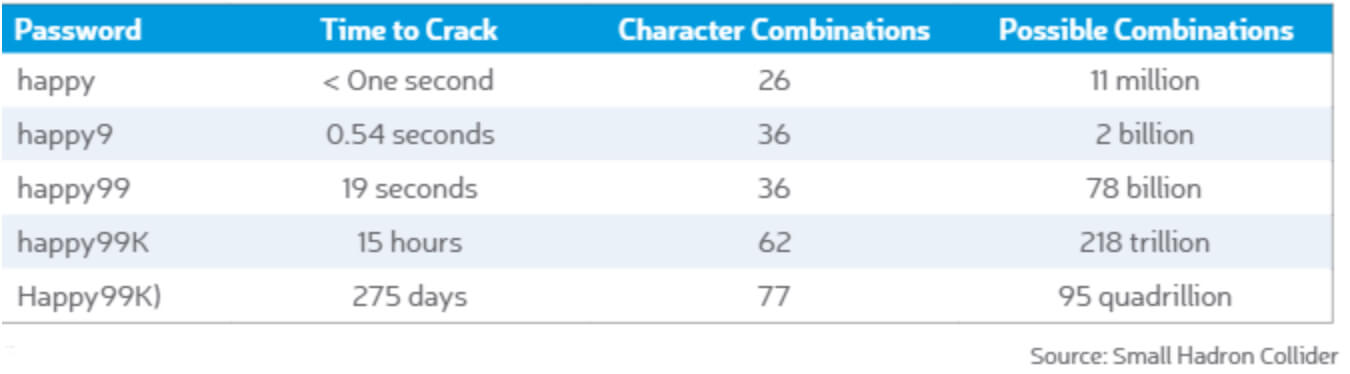
CHANGE YOUR PASSWORD FREQUENTLY
The best way to ensure your password safety is to set a calendar reminder for every 90 days.
UNIQUE PASSWORDS
Use a different password for each system. No, we really mean it. The same passwords on multiple systems increases the number of places that a cyber criminal can gain access to.
INTENTIONALLY WRONG INFORMATION
This is one of our favorite tips we’ve learned over the years. Many systems and websites force you to answer security questions like, “What’s your mother’s maiden name?” We hate to tell you this but many of the answers to these questions are searchable online, especially since social media exists. So there’s no better way to avoid threats by giving the wrong answers. An added precaution is to do different wrong answers per system, as well.
AUTHENTICATION
This is the process of verifying you are who you say you are when attempting to log into a website or system. While the level of authentication should depend on the type of data it’s protecting, we wanted to share a list of options available.
Two Factor Authentication: The most common type of authentication which requires 2 different verification modes to gain access. An example would be an ATM that requires both a card and PIN.
Out-of-Band Authentication: Uses 2 different communication modes to verify you are who you say you are. An example would be entering your login credentials on a website and then entering a code sent to your phone.
Challenge/Response: This requires you to enter questions you’ve previously entered into the system or website. An example would be a bank requiring you enter your username, then answer several security questions, followed by your password.
Images or Patterns: Also known as CAPTCHA, this requires you to enter letters and/or numbers that are provided in an image. This prevents robots or automated dictionary attacks from gaining access. As much as we all joke about “not being a robot,” this method is very effective at keeping your information safe.
Biometrics: Just like a sci-fi movie, this type of security requires biological characteristics like your fingerprint, iris, face or voice to access a system. They’re difficult to spoof but can also result in false rejections. While it seems overkill for most systems, it is something to keep in mind if your company holds confidential data.
EMAIL:
When you hear people talk about cybersecurity or cyber attacks, usually they’re thinking about emails. And it’s for good reason since emails are the most common method for distributing phishing attacks.
Since this is a topic all but beaten into you, we’ll be short with it.
- Be skeptical of any emails you receive and go with your gut feeling.
- Be careful when reviewing quarantined messages since the spam filters aren’t usually wrong.
- Don’t click before you’re certain that the link or attachment is safe
CONSUMER FILE SYNC AND SHARE TOOLS:
Tools like Microsoft OneDrive, Dropbox, and Google Drive allow you to make files available on various devices and computers, but they are an easy target for malware. Ensure that any device you may use to access these files have the same level of security. This is especially important for those that work from home often.
MOBILE DEVICES:
This category doesn’t just include smartphones, but tablets too. While they are incredibly useful for their mobility, they are one of the easier ways cybersecurity can be breached. Here are some ways to defend yourself and your data:
- Use password protection
- Disable auto username and password completion (no matter how tempting)
- Always install security updates
- Be sure you can wipe your data if the device is lost or stolen
- Be careful when using public wi-fi networks since they are less secure
- Use a hotspot on a trusted phone or encrypted VPN
- Disable file sync and share when connected to a public network
- Be careful when entering sensitive or confidential information. Only go to website urls that begin with “https”
- Use only safe stores such as Apple or Google Play.
- If you can get segmented technologies, then do it. This means that if you need to wipe data because you leave the company, then your personal data stays but the company data goes.
SOCIAL MEDIA:
We’re sure you’ve at least heard a mention of Facebook’s issues when dealing with personal information of its users. This is unfortunately just the tip of the iceberg. Personally and professionally it can help you connect with anyone around the world, but that has its negative effects too.
Not only can social media accounts be hacked by cyber criminals through the social platforms, but they also can get in through connected third-party apps and password cracking.
Twitter is a prime example of a need for shorter urls to share around. While this may be helpful to disseminating information, it’s risky to just click right away on a link you see on your feed. It’s much easier these days for links to disguise a malicious site.
Malvertising is rampant on social media platforms and it’s only getting worse. When in doubt, don’t click the link. Social media is also a breeding ground for scams and offers that trick users into revealing sensitive information. Don’t be surprised to learn that your friend or family member has bought something through an Instagram ad, only to learn they’ve been had and are out $50.
THE BEST METHODS TO DEFEND YOURSELF:
Don’t overshare information: You’ve heard the advice to avoid posting your vacation schedule on your Facebook profile, else your home might be robbed. It’s the same idea when it comes to your location, vacation photos, medical conditions, or any post that could be used against you. It’s best to limit who can see your profile or posts which can be changed in the settings of your social media account.
Turn off location services: Even if you don’t say or tag where you are, there’s still a way for metadata to be accessed from photos or videos posted online. Make sure your social profiles (and mobile apps for that matter) don’t automatically have access to your location without you knowing.
Turn on Out-of Band-Authentication: As stated above, this will require a code entered in addition to you logging in.
Be careful when clicking, liking or sharing: Doing any of these could inadvertently distribute malware or spam to others in your social networks.
Create a company social media policy: Ensure that any social media activity on behalf of your business adheres to a company policy of etiquette and privacy.
We hope that with all this information you’re ready and willing to set up cyber training for your current and future employees. When employees are aware of security threats and what to do when a threat appears, you’re strengthening the safety of your company.
So while they might end up being the primary target of a cyber criminal, you have the opportunity to turn them into the first line of defense. Keeping your defense strong requires the whole company.
Here at NorthEast Insurance Services, we’re more than insurance. We protect what means the most to you and we’ve built our business on connecting with our clients. Choosing an agent to whom you will entrust the future of your home, valuables, business and even your family should be more than just an internet search away. If this is what you are looking for in an insurance agent, then you’ve come to the right place. Don’t wait another minute and contact us today at (732) 972-1771 or Toll Free at (800) 290-8120. Visit our Contact Us page for more information!
